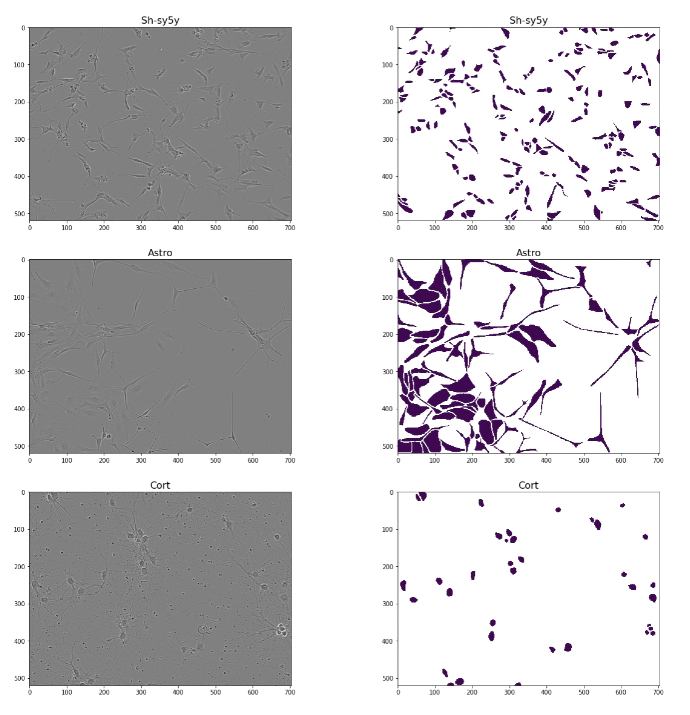
 Inference result showcase
Inference result showcaseNeurological disorders have caused increasing death and disability across the globe, which increases the demand for corresponding treatment and rehabilitation. As a key step in neurological disorders drug development, neuronal cells segmentation in light microscopy is vital to obtain deadly disorders’ response to treatment. However, common manual neuronal cells instance segmentation is inefficient, time-intensive, and labor-costing. To automatically and accurately segment neuronal cells from images, we developed a neuronal cells instance segmentation system, including an instance segmentation model based on Cascade Mask R-CNN X152 and a customized post- processing pipeline.
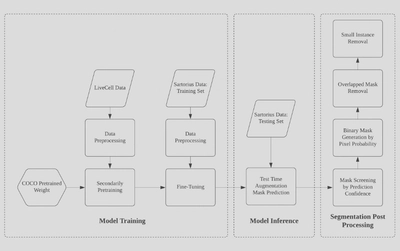
In this project, we first adopted various training skills like large-scale training, multi-scale jittering, copy-paste augmentation and etc to train a robust baseline based on Cascade Mask R-CNN X152. According to the characteristics of the dataset, we implemented several effective post process methods such as mask screening, overlapping removal, small instance removal and etc to reduce false positives. We conducted model inference on the unlabeled data set, LiveCell, to get the peseudo-label in a semi-supervised way. After screening semi-supervised data by prediction confidence, we combine them into a bigger training set and conduct multiple rounds fine-tuning by repeating the previous steps. Finally, to avoid the negative effect of naively fuse instance segmentation models, we invented a cascade IoU screening method to fuse the prediction results from six models of different folds and seeds to get the final result. Test time augmentation included flipping and resize are used in the all inference process.
The resulting robust segmentation system leverages several techniques to achieve 33.5% mAP and 34.5% mAP on the public and private leaderboard, leading to the top 1% place on Kaggle Sartorius Cell Instance Segmentation Competition. This work potentially provides an efficient and effective alternative for manually segmenting neuronal cells, which saves labor costs and further facilitates drug development in curing neurological disorders.