 Autonomous Causal Analysis with Causal-Copilot
Autonomous Causal Analysis with Causal-CopilotThe Challenge
Causal analysis is fundamental to scientific discovery and evidence-based decision-making. However, despite rapid advances in causal learning methods, a significant gap remains between theoretical sophistication and practical applicability. Domain experts often cannot leverage these powerful tools due to:
- Algorithmic complexity: 20+ methods with distinct assumptions and hyperparameters
- Steep learning curves: Requiring expertise in both causal theory and implementation
- Configuration challenges: Selecting appropriate methods for specific data characteristics
Our Solution
Causal-Copilot is an LLM-powered autonomous agent that democratizes causal analysis by automating the entire analytical pipeline. Users simply upload their data and describe their analysis goals in natural language—Causal-Copilot handles the rest.
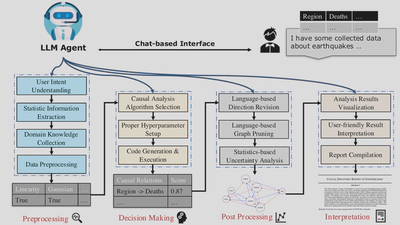
System Architecture
Causal-Copilot is built on a modular architecture with five core components:
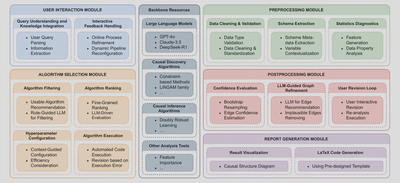
| Module | Function |
|---|---|
| User Interaction | Natural language query parsing, domain knowledge integration, interactive feedback loop |
| Preprocessing | Data cleaning, schema extraction, statistical diagnostics (linearity, stationarity, heterogeneity) |
| Algorithm Selection | LLM-guided filtering, ranking based on data characteristics, hyperparameter configuration |
| Postprocessing | Bootstrap confidence evaluation, LLM-guided graph refinement, user revision loop |
| Report Generation | Causal graph visualization, result interpretation, LaTeX report compilation |
Supported Algorithms
Causal-Copilot integrates 20+ state-of-the-art algorithms across three categories:
Causal Discovery
| Family | Algorithms | Data Type |
|---|---|---|
| Constraint-based | PC, FCI, CD-NOD, PCMCI | Tabular & Time Series |
| Score-based | GES, FGES, XGES, GRaSP | Tabular |
| Continuous Optimization | NOTEARS, GOLEM, CALM, CORL, DYNOTEARS | Tabular & Time Series |
| LiNGAM Family | ICA-LiNGAM, DirectLiNGAM, VAR-LiNGAM | Tabular & Time Series |
| MB-based | InterIAMB, IAMBnPC, HITON-MB, BAMB | Tabular |
| Granger Causality | Linear & Nonlinear Granger | Time Series |
Causal Inference
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Double Machine Learning | LinearDML, SparseLinearDML, CausalForestDML |
| Doubly Robust Learning | LinearDRL, SparseLinearDRL, ForestDRL |
| Instrumental Variables | DRIV Family (Linear, Sparse, Forest) |
| Matching Methods | PSM, CEM |
| Counterfactual | DoWhy-based counterfactual estimation |
Auxiliary Analysis
- Feature Importance: SHAP-based attribution
- Anomaly Attribution: Causal structure-based root cause analysis
Performance
Causal-Copilot consistently outperforms individual algorithms across diverse scenarios:
Tabular Data (F1 Score)
| Scenario | Causal-Copilot | PC | FCI | GES | DirectLiNGAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default (p=10, n=1000) | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.22 |
| Dense Graph (p=0.5) | 0.65 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 0.40 | 0.26 |
| Large Scale (p=50) | 0.94 | 0.70 | 0.79 | N/A | 0.23 |
| Super Large (p=100) | 0.90 | 0.68 | 0.74 | N/A | N/A |
| Extreme Large (p=500) | 0.60 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Non-Gaussian Noise | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.57 |
| Heterogeneous Domains | 0.77 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.40 | 0.23 |
| Measurement Error | 0.86 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.28 |
Time Series Data (F1 Score)
| Scenario | Causal-Copilot | PCMCI | DYNOTEARS | VARLiNGAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (p=5, l=3) | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| Large Lag (l=20) | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| Very Large (p=100) | 0.18 | N/A | N/A | 0.12 |
Interactive Demo
Try it yourself on Hugging Face Space.
Sample Output
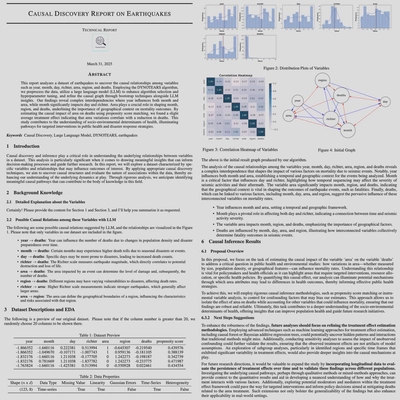
Quick Start
# Command-line usage
python main.py --data_file data.csv --apikey YOUR_KEY --initial_query "Discover causal relationships"
# Web interface deployment
python Gradio/demo.py
Citation
@article{causalcopilot2025,
title={Causal-Copilot: An Autonomous Causal Analysis Agent},
author={Wang, Xinyue and Zhou, Kun and Wu, Wenyi and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.13263},
year={2025}
}